cDeteriorationuses of crop varieties and their control; Maintenance of genetic purity during seed production
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
Deteriorationuses of crop varieties and their control; Maintenance of genetic purity during seed production
)
सामान्य परिचय (General Introduction):-Deterioration
· बीज उत्पादन का मुख्य उद्देश्य आनुवंशिक रूप से शुद्ध व अच्छी गुणवत्ता वाले बीज उत्पन्न करना होता है।
(The main objective of seed production is to produce genetically pure and good quality seeds.)
· किस्म (Variety):- यह पौधों का एक समूह है जिसमें स्पष्ट विभेदित लक्षण पाये जाते हैं। जब ये पौधे अलैंगिक या लैंगिक जनन करते हैं तो इन लक्षणों को बनाए रखते हैं।
(It is a group of plants with clear distinguished characters. These plants retain these characters upon asexual or sexual reproduction.)
· अपक्षय (Deterioration):- बीज उत्पादन के दौरान फसली किस्म की आनुवंशिक शुद्धता में हानि को अपक्षय कहते हैं। बीज उत्पादन के दौरान बहुत से ऐसे कारक होते हैं जो आनुवंशिक शुद्धता की हानि करते हैं।
(Loss of genetic purity of crop variety during seed production is called deterioration. During seed production, there are many factors that cause loss of genetic purity.)
अपक्षय के कारण (Causes of Deterioration):-
1. विकासात्मक विभिन्नताएँ (Developmental Variations)
2. भौतिक मिश्रण (Mechanical Mixture)
3. उत्परिवर्तन (Mutations)
4. प्राकृतिक परपरागण (Natural Crossing)
5. आनुवंशिक बहाव (Genetic Drift)
6. रोग का चयनित प्रभाव (Selective Influence of disease)
7. अनुचित बीज प्रमाणीकरण (Improper Seed Certification)
1. विकासात्मक विभिन्नताएँ (Developmental Variations):-
· जब बीज फसलों को कठिन वातावरणीय परिस्थितियों में उगाया जाता है तो कई पीढ़ियों के पश्चात उनके वृद्धि स्वभाव में विविधताएँ आ जाती हैं।
(When seed crops are grown under difficult environmental conditions, than after several generations, their growth patterns get changed.)
· इसे रोकने के लिए किस्मों को हमेशा अनुकूलित वातावरण में उगाना चाहिए।
(Varieties should always be grown in adapted environment to prevent this change.)
2. भौतिक मिश्रण (Mechanical Mixture):-
· खेत संदूषण (Field Contamination):- अपने आप उगे बीज या नैसर्गिक पौधे अशुद्धियाँ उत्पन्न करते हैं।
(Self sown seeds or volunteer plants produce impurities.)
· बीज ड्रिल (Seed Drill):- यदि 2 या 3 किस्मों की बुवाई के लिए एक ही बीज ड्रिल मशीन का उपयोग किया जाये तो अशुद्धियाँ आ सकती हैं।
(If the same seed drill machine is used for sowing 2 or 3 varieties, impurities can occur.)
· दो भिन्न किस्मों के बीजों को साथ साथ रखने से अशुद्धि उत्पन्न हो सकती है।
(Holding two different seed varieties together can result in impurities.)
· दो भिन्न किस्मों के बीजों को साथ साथ उगाने से अशुद्धि उत्पन्न हो सकती है।
(Growing two different seed varieties together can be produce impurities.)
· एक ही थ्रेशिंग फर्श के उपयोग से अशुद्धि उत्पन्न हो सकती है।
(Impurities can occur with the use of same threshing floor.)
· एक ही कम्बाइन या थ्रेशर के उपयोग से अशुद्धि उत्पन्न हो सकती है।
(Impurities can occur with the use of same combine or thresher.)
· उन्हीं थैलों का उपयोग बार बार करने से अशुद्धि उत्पन्न हो सकती है।
(Impurities can be caused by using the same bags again and again.)
· बीज संसाधन के दौरान अशुद्धि उत्पन्न हो सकती है।
(Impurities may occur during seed processing.)
· इससे बचने के लिए फसल वृद्धि की विभिन्न अवस्थाओं पर बीज खेत की रोगिंग करना आवश्यक होता है।
(To avoid this, it is necessary to rogue out the seed field at different stages of crop growth.)
3. उत्परिवर्तन (Mutations):-
· यह अधिक महत्व की नहीं होती है क्योंकि स्वत:उत्परिवर्तन बहुत कम उत्पन्न होते हैं। (आवृति = 10 –7)
[This is not of much importance because spontaneous mutations occur very rarely. (Frequency = 10 –7)]
· यदि किसी पौधे में दृश्य उत्परिवर्तन को देखा जाये तो उसे रोगिंग के द्वारा हटा देना चाहिए।
(If visible mutation is observed in a plant, it should be removed by rogueing.)
4. प्राकृतिक परपरागण (Natural Crossing):-
· लैंगिक रूप से प्रवर्धित फसलों में यह संदूषण का एक महत्वपूर्ण स्त्रोत है।
(It is an important source of contamination in sexually propagated crops.)
· इसमें असम्बन्धित स्टॉक या जीन प्रारूप से जीन फसल में समावेशित हो जाते हैं।
(In this, genes from unrelated stocks or genotypes are introduced into the crop.)
· यह संदूषण प्राकृतिक परनिषेचन की मात्रा पर निर्भर करता है।
(This contamination depends on the amount of natural cross fertilization.)
· परपरागित फसलों में यह संदूषण का मुख्य स्त्रोत है।
(It is the main source of contamination in cross pollinated crops.)
· यह संदूषण जाति के प्रजनन तंत्र पर निर्भर करता है –
(This contamination depends on the breeding system of the species -)
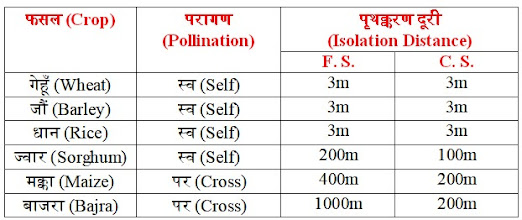
i. पृथक्करण दूरी (Isolation Distance)
ii. किस्मीय भार (Varietal Mass)
iii. परागण कारक (Pollinating Agent)
· इस समस्या से बचने के लिए पृथक्करण दूरी को बनाकर रखा जाता है।
(To avoid this problem the isolation distance is maintained.)
5. आनुवंशिक बहाव (Genetic Drift):- जब बीजों को बड़े क्षेत्रों में गुणित किया जाता है तो बीज की छोटी मात्राओं को लेकर अगले वर्ष बुवाई के लिए संरक्षित करके रखते हैं। उपरोक्त sub – sampling के कारण सभी जीन प्रारूप अगली पीढ़ी में प्रदर्शित नहीं हो पाते, जिससे आनुवंशिक संगठन में परिवर्तन आ जाता है। इसे आनुवंशिक बहाव कहते हैं।
(When seeds are multiplied over large areas, small quantities of seeds are preserved for sowing the next year. Due to this sub-sampling, all genotypes are not represented in the next generation, causing a change in genetic organization. This is called genetic drift.)
6. रोग का चयनित प्रभाव (Selective Influence of disease):-
· पर्णीय रोग में संक्रमित प्रकाश संश्लेषी ऊतक से कार्बोहाइड्रेट की बहुत कम सप्लाई होने के कारण बीज के आकार पर प्रभाव पड़ता है।
(In case of foliar disease, the size of the seed is affected by the very poor supply of carbohydrates from infected photosynthetic tissue.)
· बीज व मृदा जन्य रोग (Seed and Soil Borne Diseases):-
i. Downy mildew
ii. Ergot of Jowar
iii. Smut of Bajra
iv. Bunt of Wheat
इन रोगों में जब एक बार फसल संक्रमित हो जाती है तो इनके बीजों का वाणिज्यक उद्देश्य के लिए उपयोग खतरनाक होता है।
(In these diseases, once the crop is infected, the use of its seeds for commercial purposes is dangerous.)
· नई फसली किस्में नए रोगों के प्रति अधिक संवेदी बन सकती है। इससे ये किस्में बीज उत्पादन प्रोग्राम से बाहर हो जाती है।
(New crop varieties can become more susceptible to new diseases. This excludes these varieties from the seed production program.)
· इस समस्या से बचने के लिए मुख्य कीटों व रोगों से उचित पादप सुरक्षा करनी चाहिए।
(To avoid this problem, proper plant protection should be done from the main pests and diseases.)
7. अनुचित बीज प्रमाणीकरण (Improper Seed Certification):-
· यह प्रत्यक्ष अपक्षय कारक नहीं है।
(This is not a direct deterioration factor.)
· यदि उपरोक्त 6 कारकों में से कोई भी अपक्षय कर रहा हो तथा बिना चैक किए ही बीज प्रमाणीकरण कर दिया जाये तो फसली किस्मों का अपक्षय हो सकता है।
(If any of the above 6 factors are deteriorating and the seeds are certified without checking, then crop varieties may be deteriorated.)
बीज उत्पादन के दौरान आनुवंशिक शुद्धता का अनुरक्षण (Maintenance of genetic purity during seed production.):-
1. बीज स्त्रोत का नियंत्रण (Control of Seed Source)
2. पृथक्करण (Isolation)
3. बीज खेतों को रोगिंग (Rouging of Seed Fields)
4. बीज प्रमाणीकरण (Seed Certification)
5. ग्रो आउट परीक्षण (Grow Out Test or GOT)
1. बीज स्त्रोत का नियंत्रण (Control of Seed Source):-
· बीज फसल को तैयार करने के लिए स्वीकृत स्त्रोत से बीज वर्ग का चयन करना चाहिए।
(For preparing seed crop, seed class should be selected from the approved source.)
· बीज के 4 वर्ग हैं जो AOSCA (Association of Official Seed Certification Agency) के द्वारा दी गई व परिभाषित की गई हैं –
[There are 4 classes of seeds that are given and defined by the AOSCA (Association of Official Seed Certification Agency) -]
i. नाभिक बीज (Nucleus Seed)
ii. प्रजनक बीज (Breeder Seed):- इसके उत्पादन के लिए नाभिक बीज का उपयोग करना चाहिए।
(Nuclear seed should be used for its production.)
iii. आधार बीज (Foundation Seed):- इसके उत्पादन के लिए प्रजनक बीज का उपयोग करना चाहिए।
(Breeder seed should be used for its production.)
iv. प्रमाणीकृत बीज (Certified Seed):- इसके उत्पादन के लिए आधार बीज का उपयोग करना चाहिए।
(Foundation seed should be used for its production.)
2. पृथक्करण (Isolation):-
· बीज खेत की अन्य बीज खेत से एक निश्चित दूरी बनाकर रखनी चाहिए।
(The seed field should be kept away by a certain distance from the other seed field.)
· यह निम्न से बचने के लिए किया जाता है –
(This is done to avoid -)
i. बीज खेत में अन्य अवांछित प्रकारों, ऑफ प्रकारों से प्राकृतिक क्रॉसिंग
(Natural crossings with other undesired types, off types in the seed field)
ii. बुवाई, थ्रेशिंग व संसाधन के दौरान भौतिक मिश्रण
(Physical mixture during sowing, threshing and processing)
iii. निकटस्थ खेतों से बीज जनित रोगों के कारण संदूषण
(Contamination due to seed borne diseases from nearby fields)
· बीज की आनुवंशिक शुद्धता व अच्छी गुणवत्ता को बनाए रखने के लिए संदूषण के उपरोक्त स्त्रोतों से सुरक्षा आवश्यक है।
(Protection from the above mentioned sources of contamination is necessary to maintain the genetic purity and good quality of the seed.)
3. बीज खेतों को रोगिंग (Rouging of Seed Fields):-
· ऑफ प्रकार पादपों की उपस्थिती आनुवांशिक संदूषण का एक अन्य स्त्रोत है।
(The presence of off-type plants is another source of genetic contamination.)
· ऑफ प्रकार (Off type):- जब किसी पौधे के लक्षण बीज फसल के लक्षणों से भिन्न होते हैं तो इन्हें ऑफ प्रकार पौधे कहते हैं।
(When the characters of a plant differ from the characters of seed crop, it is called an off-type plant.)
· ऑफ प्रकारों के मुख्य स्त्रोत (The main sources of off types):-
i. निश्चित लक्षणों या उत्परिवर्तन के लिए पौधों का पृथक्करण हो जाना
(Segregation of plants for certain characters or mutations)
ii. पिछली फसलों से नैसर्गिक पौधे
(Volunteer plants from previous crops)
iii. अन्य क़िस्मों के आक्समिक रोपित बीज
(Accidentally planted seeds of other varieties)
iv. रोगी पौधे (Diseased plants)
· ऑफ प्रकार पौधों को पुष्पन से पहले ही रोगिंग के द्वारा हटा देना चाहिए ताकि वे परागण न कर सकें। इसके लिए प्रशिक्षित व्यक्ति का नियमित पर्यवेक्षण आवश्यक है।
(Off-type plants should be removed before flowering so that they do not pollinate. For this, regular supervision of trained person is necessary.)
4. बीज प्रमाणीकरण (Seed Certification):-
· इसका मुख्य उदेश्य किसानों को अच्छी गुणवत्ता के बीज उपलब्ध कराना है।
(Its main objective is to provide good quality seeds to the farmers.)
· इसे उदेश्य को पूर्ण करने के लिए बीज प्रमाणीकरण संस्था (SCA) का प्रशिक्षित व्यक्ति फसल वृद्धि की उपयुक्त अवस्थाओं पर खेत का निरीक्षण करता है।
(For this purpose, a trained person from the Seed Certification Agency (SCA) inspects the field at appropriate stages of crop growth.)
· बीज संसाधन के पश्चात बीज ढेर से बीज के नमूने लेकर बीज परीक्षण प्रयोगशाला को भेजता है।
(After seed processing, the seed samples are collected from the seed lot and sent to the seed testing laboratory.)
· गुणवत्ता की पुष्टि होने के बाद ही बीज का प्रमाणीकरण किया जाता है।
(Seed certification is done only after the confirmation of the quality.)
5. ग्रो आउट परीक्षण (Grow Out Test or GOT):-
· बीज उत्पादन के लिए उगाई गई किस्में आनुवंशिक शुद्धता के लिए समय समय पर चैक होनी चाहिए। इसके लिए GOT का उपयोग किया जाता है।
(Varieties grown for seed production should be checked periodically for genetic purity. GOT is used for this purpose.)
· इससे यह सुनिश्चित किया जाता है कि ये किस्में सत्य रूप में अनुरक्षित हैं।
(This ensures that these varieties are maintained in true form.)
· संकर बीज उत्पादन में GOT अनिवार्य होता है।
(GOT is essential in hybrid seed production.)
i. हाथ द्वारा विपुंसन व परागण कराते हैं।
(Performs hand emasculation and pollination.)
ii. जनक वंशक्रमों की शुद्धता का परीक्षण करते हैं।
(Test the purity of the parent lines.)
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
Comments
Post a Comment