Seed Certification, Phases of Certification, Procedure for Seed Certification, Field Inspection
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
बीज प्रमाणीकरण (Seed Certification):-
1. परिचय (Introduction):-
· परिभाषा (Definition):- यह एक ऐसी प्रक्रिया है जो बीज प्रमाणीकरण के दौरान बीज गुणवत्ता का अपक्षय करने वाले सभी कारकों को प्रभावी रूप से नियंत्रित करती है।
(It is a process that effectively controls all the factors that deteriorate seed quality during seed production.)
· उद्देश्य (Objective):- बीज प्रमाणीकरण का मुख्य उद्देश्य किसानों को उच्च गुणवत्ता सम्पन्न बीज उपलब्ध कराना है ताकि किसान अधिक आर्थिक लाभ प्राप्त कर सकें।
(The main objective of seed certification is to provide high quality seeds to the farmers so that farmers can get more economic benefits.)
· केवल Notified किस्में ही बीज प्रमाणीकरण के लिए योग्य होती हैं। बिना Notification के बीज का प्रमाणीकरण संभव नहीं है।
(Only notified varieties are eligible for seed certification. Certification of seeds without notification is not possible.)
2. भारत में बीज प्रमाणीकरण का विकास (Progress of seed certification in India):-
· भारत में बीज प्रमाणीकरण की शुरुआत 1963 में National Seed Corporation की स्थापना के साथ हुई।
(Seed certification in India began in 1963 with the establishment of National Seed Corporation.)
· 1966 में Seed Act पास हुआ।
(The Seed Act passed in 1966.)
· 1971 में बीज मानक बनाए गए और बीज प्रमाणीकरण के लिए विभिन्न राज्यों में State Seed Certification Agencies की स्थापना की गई।
(Seed standards were made in 1971 and State Seed Certification Agencies were established in various states for seed certification.)
3. बीज प्रमाणीकरण संस्था के लिए शर्तें (Conditions for Seed Certification Agency):-
· स्वायत काय (Autonomous body):- यह किसी अन्य संस्था के नियंत्रण में नहीं होनी चाहिए। इसका कार्य स्वतंत्र होना चाहिए।
(It should not be under the control of any other institution. Its function should be independent.)
· इसे बीज के उत्पादन व विपणन में भाग नहीं लेना चाहिए।
(It should not participate in the production and marketing of seeds.)
· इसे सम्पूर्ण देश में उपयोग किए जाने वाले प्रमाणीकरण मानकों को मानना चाहिए ताकि एकरूपता बनाकर रखी जा सके।
(It should follow the certification standards used throughout the country so that uniformity can be maintained.)
· इसे न लाभ न हानि के सिद्धान्त पर कार्य करना चाहिए। ताकि यह ईमानदारी से कार्य कर सके।
(It should work on the principle of neither profit nor loss. So that it can work honestly.)
4. बीज प्रमाणीकरण की विधि (Procedure of Seed Certification):- इसके 4 मुख्य चरण होते हैं-
(It has 4 main steps -)
a. आवेदन (Application)
b. सत्यापन (Verification)
c. निरीक्षण (Inspection)
d. टैगिंग व सीलिंग (Tagging and Sealing)
a. आवेदन (Application):- कोई भी व्यक्ति या संस्था जो प्रमाणीकृत बीज उत्पादन करना चाहते हैं उन्हें राज्य से संबन्धित SSCA में आवेदन करना होता है। यह प्रत्येक राज्य के लिए विशिष्ट होती है। उदाहरण के लिए राजस्थान में RSSOCA (Rajasthan State Seed and Organic Certification Agency) है। आवेदन के साथ निर्धारित आवेदन शुल्क जमा कराना पड़ता है।
(Any person or organization who wants to produce certified seed has to apply to the state-related SSCA. It is specific to each state. For example Rajasthan has RSSOCA (Rajasthan State Seed and Organic Certification Agency). The application has to be submitted along with the prescribed application fee.)
b. सत्यापन (Verification):-
· आवेदन प्राप्त होने पर SSCA यह सत्यापन करती है कि - बीज किस्म notify है, बीज स्त्रोत मान्य है और आवेदन फीस भरी है। तीनों आवश्यकतायें पूर्ण होने पर आवेदन को स्वीकार कर लिया जाता है। यदि उपरोक्त तीनों में से कोई एक आवश्यकता भी पूर्ण नहीं हो रही हो तो आवेदन को निरस्त किया जा सकता है।
(On receipt of the application, the SSCA verifies that the seed variety is notified, the seed source is valid and the application fee is paid. The application is accepted after all three requirements are met. If any one of the above three requirements is not being fulfilled, the application can be rejected.)
· आवेदन के स्वीकार होने पर बीज उत्पादक को कुछ अन्य शुल्क जमा करने पड़ते हैं जैसे निरीक्षण शुल्क, बीज परीक्षण शुल्क आदि। शुल्क समय के अनुसार परिवर्तित हो सकते हैं।
(On acceptance of the application, the seed producer has to pay some other fees like inspection fee, seed test fee etc. Fees may change over time.)
c. निरीक्षण (Inspection):- इसे आगे 2 प्रकारों में विभाजित किया जाता है –
(It is further divided into 2 types -)
i. खेत निरीक्षण (Field Inspection)
ii. बीज निरीक्षण (Seed Inspection)
i. खेत निरीक्षण (Field Inspection):-
· SSCA एक बीज निरीक्षक को नियुक्त करती है जो फसल वृद्धि की उपयुक्त अवस्थाओं पर खेत का निरीक्षण करता है। खेत निरीक्षण के दौरान बीज उत्पादक व बीज निरीक्षक दोनों का खेत में उपस्थित होना अनिवार्य है।
(The SSCA appoints a seed inspector who inspects the field at appropriate stages of crop growth. During the field inspection, it is mandatory for both the seed producer and the seed inspector to be present in the field.)
· सामान्यतया खेत निरीक्षण निम्न 5 फसल वृद्धि अवस्थाओं पर किया जाता है -
(Generally, field inspection is done at the following 5 crop growth stages -)
Ø बुवाई के समय
(At the time of sowing)
Ø पुष्पन से पूर्व
(Before flowering)
Ø पुष्पन के दौरान
(During flowering)
Ø फसल परिपक्वता पर
(At crop maturity)
Ø फसल कटाई पर
(At crop harvesting)
· बीज निरीक्षक खेत के निरीक्षण के दौरान निम्न कारकों को चैक करता है:-
(The seed inspector checks the following factors during field inspection:-)
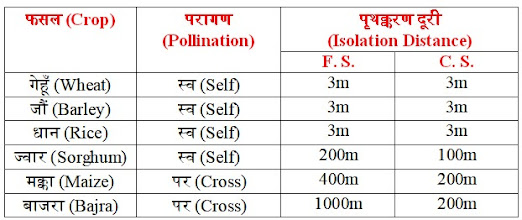
Ø पृथक्करण दूरी (Isolation distance):- इसके लिए बीज निरीक्षक खेत के चारों ओर एक चक्कर लगाता है।
(For this, the seed inspector takes a detour around the farm.)
Ø रोगिंग (Rouging):- इसके लिए बीज निरीक्षक खेत के अंदर एक स्कीम के अनुसार निश्चित पैटर्न में भ्रमण करता है। बीज निरीक्षक 6 पैटर्न में खेत में भ्रमण कर सकता है।
(For this, the seed inspector travels inside the field in a fixed pattern according to a scheme. The seed inspector can travel the field in 6 patterns.)
यदि बीज फसल का 1/3 से कम भाग संदूषित हो तो बीज उत्पादक को उचित निर्देश दिये जाते हैं ताकि वो संदूषण को हटाकर न्यूनतम खेत मानकों को बनाकर रख सके। यदि बीज फसल का 1/3 या इससे अधिक भाग संदूषित हो तो इसे निरस्त कर दिया जाता है।
(If less than 1/3 of the seed crop is contaminated, proper instructions are given to the seed producer so that he can remove the contamination and maintain minimum field standards. If 1/3 or more of the seed crop is contaminated, it is discarded.)
· यदि सभी कारक खेत मानकों के अनुरूप हों तो प्रमाणीकरण के लिए स्वीकार कर लिया जाता है। यदि कुछ कारक संदूषण उत्पन्न कर रहे हों तो बीज उत्पादक को उचित निर्देश दिये जाते हैं। यदि खेत कि सम्पूर्ण दशा खेत मानकों से भिन्न हो तो इसे निरस्त कर दिया जाता है।
(Certification is accepted if all factors conform to field standards. If some factors are causing contamination then proper instructions are given to the seed producer. If the entire state of the field differs from the field standards, it is discarded.)
· न्यूनतम खेत निरीक्षणों की संख्या (Minimum Number of Field Inspections):- आधार व प्रमाणीकृत बीज उत्पादन के लिए खेत निरीक्षणों की संख्या व फसल वृद्धि अवस्थाएँ एक फसल से दूसरी फसल में परिवर्तित हो सकती हैं।
(For foundation and certified seed production, the number of field inspections and crop growth stages may change from one crop to another.)
· खेत काउंट्स की संख्या (Number of Field Counts):- यह खेत के क्षेत्रफल के अनुसार निर्धारित की जाती है।
(It is determined according to the area of the farm.)
· प्रति काउंट पौधों की संख्या (Number of plants per count):-
· बीज निरीक्षण रिपोर्ट (Field Inspection Report):- इसकी कुल 4 प्रतियाँ बनाई जाती हैं तथा एक – एक प्रति निम्न को भेजी जाती है –
(A total of 4 copies are made and one copy is sent to the following -)
Ø बीज उत्पादक (Seed grower)
Ø मुख्य ऑफिस (Head office)
Ø क्षेत्रीय ऑफिस (Regional office)
Ø बीज निरीक्षक (Seed inspector)
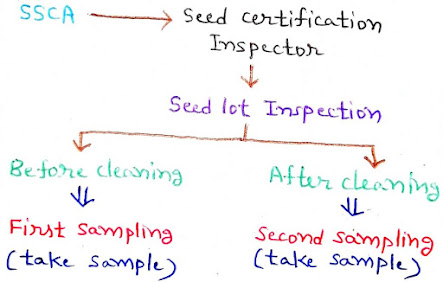
ii. बीज निरीक्षण (Seed Inspection):- बीज निरीक्षक बीज ढेर में से बीज के नमूने लेकर संबन्धित SSTL को भेजता है। SSTL में बीज की गुणवत्ता से संबन्धित परीक्षण किए जाते हैं। SSTL रिपोर्ट बनाकर बीज निरीक्षक को भेजती है। यदि बीज ढेर न्यूनतम बीज मानकों के अनुरूप होता है तो इसे प्रमाणीकरण के लिए स्वीकार कर लिया जाता है। यदि कोई कमी हो तो इसे निरस्त कर दिया जाता है।
(The seed inspector takes samples of the seed from the seed lot and sends it to the concerned SSTL. SSTL carries out tests related to seed quality. The SSTL creates the report and sends it to the seed inspector. If the seed lot conforms to the minimum seed standards then it is accepted for certification. If it does met minimum standards, it is rejected.)
d. टैगिंग व सीलिंग (Tagging and Sealing):-
· यदि SSTL की रिपोर्ट सकारात्मक आती है तो बीज ढेर को प्रमाणीकरण टैग व लेबल जारी कर दिये जाते हैं। बीज को थैलों में भरकर उन्हें सील कर दिया जाता है।
(If the SSTL report is positive, certification tags and labels are issued to the seed lot. The seeds are filled in bags and sealed.)
· प्रमाणीकरण टैग पर बीज ढेर के बारे में जानकारी दी होती है जैसे – बीज का प्रकार व किस्म, शुद्धता प्रतिशत, अंकुरण प्रतिशत, नमी प्रतिशत, प्रमाणीकरण की दिनांक, वैध्यता अवधि आदि।
(The certification tag gives information about the seed lot such as type and variety of seed, purity percentage, germination percentage, moisture percentage, date of certification, validity period, etc.)
· बीज प्रमाणीकरण 8 महीने के लिए वैध्य होता है। इस वैध्यता अवधि को 4 महीने और बढ़ाया जा सकता है।
(Seed certification is valid for 8 months. This validity period can be extended by 4 months.)
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps













Comments
Post a Comment